*Saraswati D Rajput,
* Senior Resident, Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi

Nobel Prize in Medicine 2016
Japanese cell biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 201G for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy, a fundamental process for degrading and recycling cellular components.
Biography
Born on February 9, 1945, in Fukuoka, Japan, Ohsumi earned his Ph.D. from the University of Tokyo in 1974. After conducting postdoctoral research at Rockefeller University in New York, he returned to the University of Tokyo. In 1996, he joined the National Institute for Basic Biology in Okazaki and later became a professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
Research on Autophagy
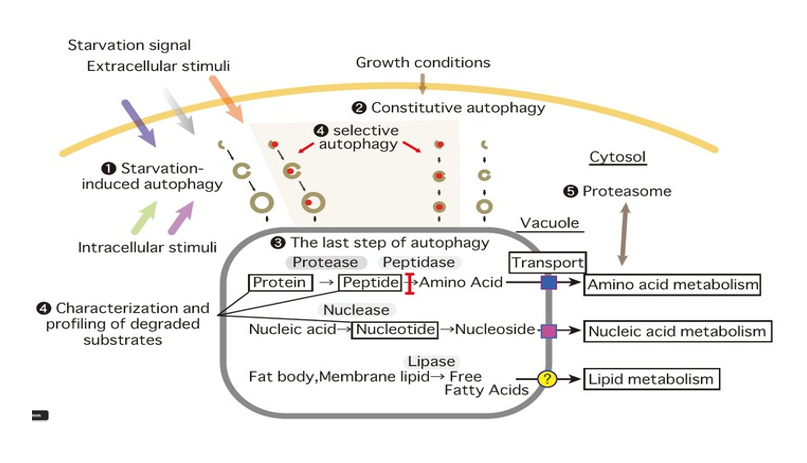
Autophagy, meaning “self-eating,” is a vital cellular process where cells degrade and recycle their own components. Ohsumi’s pioneering work in the early 1990s involved using yeast to identify genes essential for autophagy. His research illuminated how cells adapt to starvation and respond to various stresses by recycling their contents, providing insights into the role of autophagy in diseases such as cancer and neurological disorders.
Recognition and Awards
In addition to the Nobel Prize, Ohsumi has received several prestigious awards, including:
- Kyoto Prize in Basic Sciences (2012)
- Gairdner Foundation International Award (2015)
- Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences (2017)
References
- Nobel Prize (201G). The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 201G. Retrieved from https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/201G/press- release/
- Wikipedia (2025). Yoshinori Ohsumi. In Wikipedia. Retrieved January U, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yoshinori_Ohsumi
- Mizushima, N; Komatsu, M (11 November 2011). “Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues”. Cell. 147 (4): 728–41.
- Ohsumi Lab. Tokyo Institute of Technology. Available from: http:// ohsumilab.aro.iri.titech.ac.jp/english.html