B. K. Kundu Department of Medicine, ABVIMS & Dr. RML Hospital, New Delhi
https://meditropics.com/biologics-in-rheumatology/
“I don’t see how you can write anything of value if you don’t offend someone.”― Marvin Harris
- INTRODUCTION
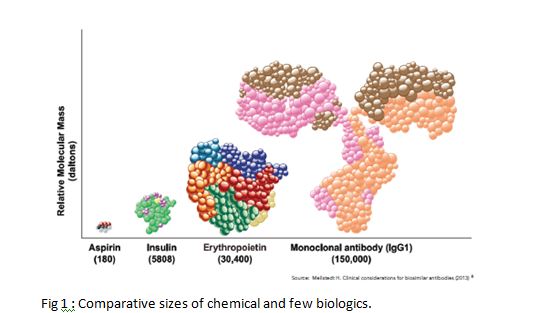
Biologic means any medicine made using a living organism. This includes Insulin, Erythropoietin, and of course our topic of discussion- biologics. Compared to ‘chemicals’, biologics are bigger in size with their weight going into 5 figure Daltons. Comparative size is shown in Figure 1.
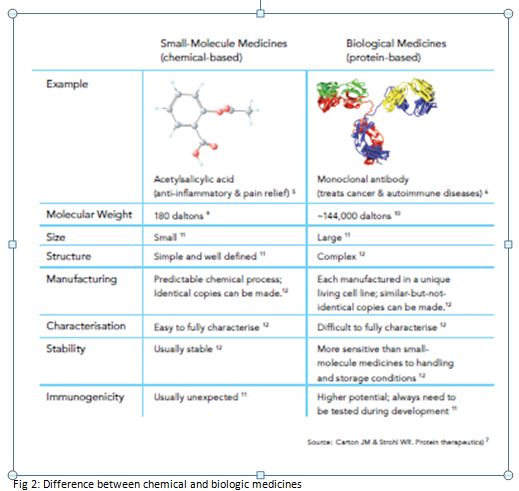
Differences between a ‘chemical’ medicine and ‘biologic’ medicine are given in Figure 2.
Most biologics in use in Rheumatology are Immunoglobulins, presently IgG. The ‘Variable’ region gives specificity, but the ‘Constant’ domains can be cloned, engineered, and mixed to generate recombinant antibody, or biologic.
Biologics are manufactured using genetic engineering in cell lines. A DNA encoding the biologic is introduced into a host cell, a process called ‘transfection’, and then integrated in the host DNA. The cells are then screened, and the clone with the best productivity is selected. The selected cell line is transferred to a bioreactor and a master cell line preserved, called Master Cell Bank (MCB). Working Cell Banks are then taken out from the MCB, and used for production.
Some terms need to be explained. The first biologic is called a bio-originator, or ‘reference product’
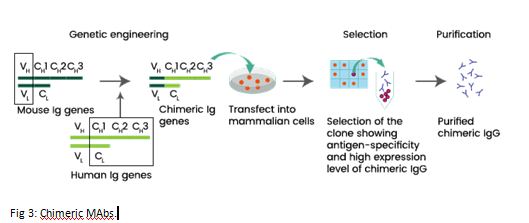
Biosimilars are legitimate copy of the bio-originator which is out of patent. It undergoes analytical and clinical assessment and is approved by a regulator. Bio mimics are intended copies but without regulatory approvals. Second generation biologics have same mechanism of action, better performance, but structurally different. Interchangeable biosimilar are ones which can be substituted for the reference product without permission of the health care provider, eg by pharmacist. Chimeric monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are composed of the murine variable region and human constant regions (Figure 3). Humanized MAbs are all regions of the mouse antibody are replaced with human counterparts except for the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), i.e., the amino acids that make direct contact with the antigen. Human MAbs are made from mice genetically altered to carry human genes. Thus, they don’t contain murine elements.
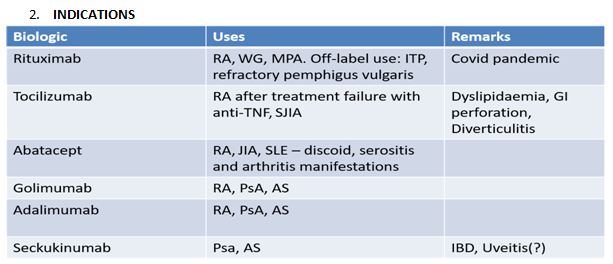
The biologics presently used in Rheumatology in India are (a) Anti TNF MAbs–Infliximab (INF), Adalimumab (ADA), Golimumab (GOL) (b) TNF receptor inhibitor Etanercept (ETA) (c) Tocilizumab (d) Abatacept (ABA) (e) Rituximab (RTX), and (f) Seckukinumab (SEC).
- CONTROVERSIES
a) Brands vs Generics
Biosimilars are developed by reverse engineering. A protein with same primary structure can be manufactured by a DNA sequence which may differ from the bioreference product, as most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. Add co-translational, post-translational, and chemical modifications, and impurities during manufacture, and we have a different molecule. Changing the biologic can induce Anti Drug antibodies, compromising the safety and efficacy of both.
b) Should we start biologics early?
In Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), initial combination of methotrexate (Mtx) with TNFi was found to have better results than Mtx monotherapy. However, the clinical superiority was found in the 1st year, and not after 2nd year, though radiological improvement was prevented. [Swefot trial Lancet 2012]. The TEAR trial confirmed neither clinical nor radiological benefit, while the NeoRACo trial negated long term benefit of TNFi. Other studies also showed similar results. The concept of ‘Induction Maintenance’ was put forward when all biologics were shown to be able to be withdrawn if used early in RA, thus giving a ‘therapeutic window of opportunity’. That bDMARDs improved radiographic outcomes for patients with early or established RA, when used in combination with MTX and to a lesser extent as monotherapy is the present opinion. [Clin Exp Rheum 2018]
In Ankylosing Spondylitis, structural progress did not depend on TNF (2008) and ADA did not impove radiology (2009) was reported. From 2013 onwards, most studies show that TNFi slowed radiology progression if used in early stages. The effect was less marked in SEC (numerically but not statistically significant). The role of NSAIDs was similarly different with initially being though to delay radiographic progression, but later not to individually but in combination with TNFi, with best improvements in acute phase reactants. The latest opinion staes that TNFI gives benefit after 4 years of consistent use and NSAIDs and Sec don’t change radiologic progression. {A&R 2020].
c) How frequently should we monitor?
Too frequent monitoring to achieve treatment targets leads to overuse of glucocorticoids and biologics. Studies show that in these cases, significant proportion of cases will require biologics.
d) Which biologic to use?
A review of network meta-analysis comparing biologics in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritisshow that the appropriate biological first-line therapy has not yet been identified. [European review for Medical and pharmacological sciences, 2020]
d) Are biologics worth it?
The high incremental cost and the small, non-significant difference in effectiveness resulted in high Incremental Cost Effectiveness Ratio (ICER), thus suggesting that biologics are not cost-effective. [Rheumatology 2016].
e) Off label use in SLE
The only biologic recommended in SLE is Belimumab. But RTX is used off label in many situations. Initially though to worsen Lupus Nephritis (LN), it is now though to have complete or partial response in 2/3rd of patients. Also, RTX enables cessation of oral steroids completely in LN [ARD 2013].
f) LTBI Screening
Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) using 1 TU RT23-Guindy should be used. Augmented TST and 2-step TST are other methods of screening for LTBI. The 4S symptoms of fever, cough, weight loss, and night sweats with aTST and IGRA eliminates TBI in patients using biologics. Reactivation is most common with TNFi, with non-TNFi having less chances.
g) Pneumococcal vaccination- PCV13 or PPSV23
The recommendation of PPSV23 is more appropriate in those on or intended to be on biologics because it can generate a T-cell independent antibody response by directly stimulating B-cells.
h) Effect of biologics on vaccine induced antibody levels
TNFi have been found to decrease levels of antibodies but can be continued. The same holds true for TCL though it doesn’t affect antibody levels. Data is lacking about ABA, while vaccination has to be done 3 months prior or 6 months after biologic. Similarly, for covid vaccinations, ABA should be held up for 1 week for IV and 2 weeks for SC administration. There is no consensus regarding SEC, TCL, and TNFi. Those for RTX remains same. [Jan 28, ACR 2022, 5th review]
i) What if a patient needs surgery?
For elective surgery, the rule of thumb is that the surgery must be delayed for 1 weeks after the next dose of the biologic becomes due, except for RTX and SEC for which it is 4-7 months after the last dose and 3 months after the last dose, respectively. Dosing interval or half-life characteristics can be used for this calculation. For major surgeries, 5 half lives can be allowed to elapse before performing surgery.
j) What if the patient becomes pregnant? And what about lactating mothers?
INF should be stopped at 16 weeks, while ADA and ETA can be continued till 3rd trimester. All others have to be stopped at or before conception. Similarly, RTX and TNFi are strongly compatible with lactation.