PSEUDO-THROMBOCYTOPENIA: IMPORTANCE OF PERIPHERAL SMEAR
https://meditropics.com/cr3-2022-2/
INTRODUCTION
Pseudo-thrombocytopenia is often an unrecognised laboratory phenomenon that leads to misinterpretation of laboratory values and extensive workup of the patient including bone marrow studies. The use of coulter machines for analysis of blood count has made us analyse samples at a faster rate but simple microscopic examination can help in ruling out a common phenomenon of Pseudo-thrombocytopenia. Although modern coulter machines can detect platelet clumping, but is not very specific and often inaccurate.
We present a case of EDTA induced Pseudo-thrombocytopenia and how a simple peripheral smear can help in the diagnosis of this phenomenon.
KEY WORDS-EDTA, Pseudo-thrombocytopenia
CASE REPORT
21-year-old unmarried lady, presented in the OPD with loss of scalp hair for 3 months. No history of any bleeding diathesis, fever. There was no co-morbidity and the patient denied use of any medication.
On examination, built and nutrition was normal (BMI 22 kg/m2). Pallor was present. On examination, there was diffuse scalp hair loss. Rest of the examination was within normal limits.
Complete blood count showed Hb: 10.6 gm%; TLC: 9,600/cumm; Platelets: 14,000/cu.mm; Haematocrit: 32%, Renal and Liver Function tests was within normal limits. Chest X Ray, Ultrasound of Whole Abdomen and ECG was done which was normal. Thyroid Profile TSH: 2.32 (0.3-5.6) µIU/mL; FT4: 0.9 (0.6-1.12) ng/dL; FT3: 2.9 (2.5-3.9) pg/mL. Vitamin B12: 198 (180-914) pg/mL. Folic Acid Levels: 32.89 (6.5-35) mmol/L. Iron Profile: Iron: 48 (60-150) µg/dL; TIBC: 359 (250-400) µg/dL; Sat%: 13.4 (20-35) %; Ferritin: 17.9 (11-307) ng/mL.
For Thrombocytopenia complete infective and auto-immune workup was done, all of which came out to be negative. Peripheral Smear (EDTA vial) showed platelets in clumps.
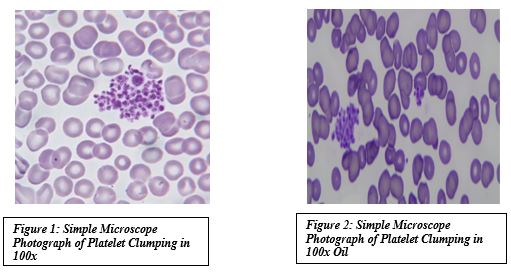
Despite severe thrombocytopenia patient had no bleeding tendency, so repeat whole blood was sent in Citrate and Heparin tube which showed Hb: 10.5 gm%; TLC: 9,100/cmm; Platelets: 1,92,000/cu.mm; Haematocrit: 29%.
Hence, EDTA dependent thrombocytopenia was confirmed.
DISCUSSION
EDTA dependent thrombocytopenia or pseudo-thrombocytopenia was first reported by Gowland et al in the year1969. It is a laboratory phenomenon with prevalence of 0.1%–2% in hospitalized patients. It is due to in vitro agglutination of platelets in the vacutainer caused by IgM/IgG/IgA autoantibodies directed against epitopes on platelet surface glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa. EDTA induces a conformational change in GPIIb/IIIa, exposing these epitopes and resulting in platelet agglutination. The use of an alternate anticoagulant, such as citrate or heparin, may be helpful. Although up to 20% of patients with EDTA-Thrombocytopenia also show this phenomenon with citrate. To prevent this, blood should be sent in Citrate or Heparin tube also.
CONCLUSION
Unrecognized Pseudo-Thrombocytopenia may result in unnecessary laboratory testing and unwarranted interventions. Examination of a well-prepared peripheral blood smear is mandatory for every case of thrombocytopenia to rule out platelet clumping. For a definitive diagnosis of EDTA thrombocytopenia, the simultaneous collection of blood in EDTA, Citrate or Heparin containing tubes may provide a simple, rapid means of identifying the presence of Pseudo-thrombocytopenia. It is therefore important to consider EDTA dependent thrombocytopenia as differential for low platelet counts in the absence of clinical symptoms of hemorrhagic diathesis.
REFERENCES:
- Lardinois B, Favresse J, Chatelain B, Lippi G, Mullier F. Pseudothrombocytopenia—A review on causes, occurrence and clinical implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021;10(4):594.
- Barbara A. Konkle. Disorders of platelets and vessel wall. In: J Larry Jameson, Denis L. Kasper, Dan L. Longo, Anthony S. Fauci, Stephen L. Hauser, Joseph Loscalzo(Eds). Harrisonʾs principle of internal medicine. 20thMc Graw Hill Education. 2018;p822-829.